Speed and acceleration:
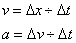
where:
v is velocity
x is displacement (or distance)
t is time
a is acceleration
Uniformly accelerated motion:
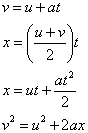
where:
v is final velocity
u is initial velocity
x is displacement (or distance)
t is time
a is acceleration
Momentum and force:
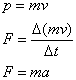
where:
p is momentum
m is mass
F is force
Δ is change in
Circular motion:
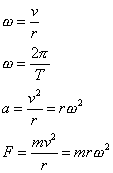
where:
ω is angular velocity
v is velocity
T is period
r is radius
F is force
m
is mass
Work and energy:
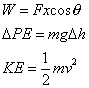
where:
g is gravitational field strength (9.81 N/kg)
W is work
PE is potential energy
KE is kinetic energy
m is mass
v
is velocity
h is height
Δ is change in
F
is force
Power and efficiency:
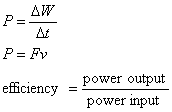
where:
P is power
Δ is change in
F is force
W is work
v is velocity
t is time
Stress and strain:
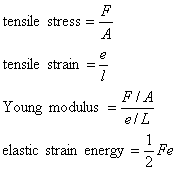
where:
A is area
e is extension
l is length
F is force
Current electricity:
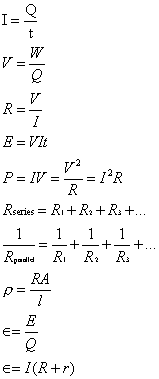
where:
Q is charge
I is current
V is voltage
R
is resistance
Є is the electro-motive
force (e.m.f)
Capacitors:
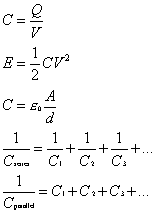
where:
C is capacitance
d is distance
V is voltage
A is area
d
is distance
E is energy
Radioactivity:
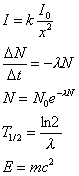
where:
I is intensity of radiation
E is energy
m is mass
T1/2
is half-life
c is light's speed (299 792 485 m/sec)
λ is wavelength
N is number of radioactive atoms
Simple harmonic motion:
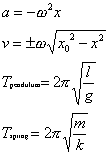
where:
T
is period
l is length of pendulum's string
x is displacement moved by pendulum
g is gravitational field strength
ω is angular velocity
v is velocity
a is acceleration
m is mass
k is spring stifness
Waves:
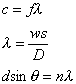
where:
f is frequency
s is fringe separation
λ is wavelength
D is distance to screen
w is slit separation
d is grate spacing
c is velocity of wave
Refraction:

where:
n is refractive index
c is speed of light in a vacuum
v is speed of light in material
θ1 is angle of incidence
θ2 is angle of refraction
Photons and duality:
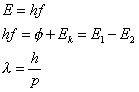
where:
Ek
is kinetic energy
E is energy
f
is frequency
p is momentum
h is Planck's constant
Φ is work function for metal
Magnetism:
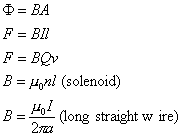
where:
Φ is flux
F is force
Q
is charge
v is velocity
μ is the permeability
of free space (constant)
n is number of turns divided by length of coil
B is field flux density
I is current
l is length of wire
Induced Current:
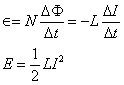
where:
N is the number of turns of a coil
is the electro-motive force (e.m.f)
L is the self-inductance (constant)
A.c. and transformers:
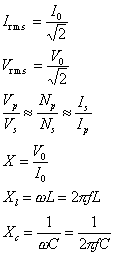
where:
N/I/Vp is primary number of turns/current/voltage
of transformer
N/I/Vs
is secondary number of turns/current/voltage
of transformer
r.m.s.
is root mean square
X is reactance
w is angular frequency
C is capacitance
Gravitation:
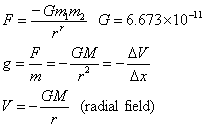
where:
g is gravitational strength
G is universal constant of gravitation
V is gravitational potential
Thermodynamics:
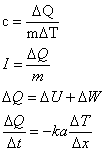
where:
c
is specific heat capacity
l is specific latent heat
Q is amount of heat transferred
T is temperature
U is internal energy
W is work done by a system
k is Boltzman' constant
Gases:
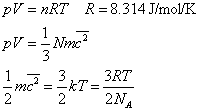
where:
p
is pressure
V is volume
N is number of particles
c is average speed of particles
n is number of moles in a gas
R is universal molar gas constant
Electrostatics:
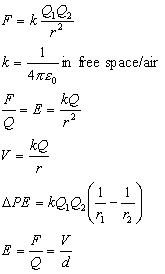
where:
F is
force
Q is charge
r is distance between 2 charged objects
ε0 is
permittivity of free space
E is energy
V is voltage
d
is distance moved by charge
ΔPE is
change in potential

